![]()
Terraform is a powerful tool that enables you to define and provision infrastructure as code. It’s highly valued for its ability to manage infrastructure consistently and reproducibly. However, working with Terraform can sometimes be challenging, especially when you encounter errors. In this article, we’ll explore common Terraform errors and provide troubleshooting tips to help you resolve these issues efficiently.
In this, we are covering these recurring errors:
- Provider Configuration Errors
- Authentication Errors
- Permission Errors
- Resource Already Exists
- Syntax Errors
- Dependency Cycle Errors
- Invalid Index
- Missing Required Argument
- Output Errors
- State Locking Errors
- AWS Service Errors
- Module Source Errors
- Network Configuration Errors
- Resource Deletion Errors
- Unsupported Attribute
- Invalid Value for Variable
- Terraform Backend Errors
- Invalid Data Source
- Resource Not Found
- Template Render Errors
- Conclusion
- FAQs
Provider Configuration Errors
Error: Failed to install provider

Solution: Ensure your provider block is correctly configured and initialized with terraform init. This command sets up the necessary plugins and prepares your environment for Terraform operations.
Authentication Errors
Error: No valid credential sources found for AWS Provider

Solution: Check that your AWS credentials are correctly configured. You can set them up using environment variables, the AWS credentials file, or IAM roles. Ensuring proper authentication is crucial for secure and successful Terraform operations.
Permission Errors
Error: Error creating IAM Role: AccessDenied

Solution: Make sure your IAM user or role has the necessary permissions to perform the actions specified in your Terraform code. This might involve adding policies or adjusting existing ones to grant the required access.
Resource Already Exists
Error: Error creating S3 bucket: BucketAlreadyExists

Solution: Use unique names for globally unique resources like S3 buckets. Since S3 bucket names must be unique across all AWS accounts, it’s essential to ensure your chosen name is not already in use.
Syntax Errors
Error: Invalid resource argument
Solution: Review your Terraform configuration files for syntax errors. Use terraform validate to help catch these errors. This command checks the syntax and internal consistency of your configuration files.
Dependency Cycle Errors
Error: Cycle: module.module_name.resource_name

Solution: Check for circular dependencies in your configuration and resolve them by adjusting dependencies or using the depends_on attribute. This ensures that Terraform can determine the correct order of operations.
Invalid Index
Error: Invalid index

Solution: Ensure that you are accessing valid indices within lists and maps. Double-check the data structures you are working with to avoid referencing non-existent elements.
Missing Required Argument
Error: Missing required argument

Solution: Verify that all required arguments for your resources and modules are provided. Missing arguments can prevent Terraform from executing correctly, so ensure every necessary parameter is specified.
Output Errors
Error: Output refers to sensitive values
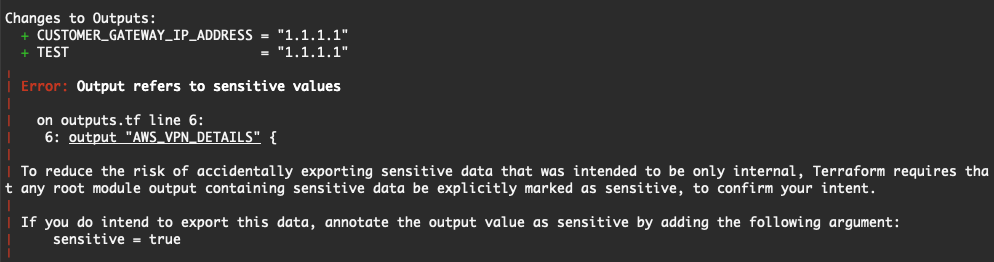
Solution: Mark the output as sensitive in your configuration if it contains sensitive information. This protects sensitive data from being exposed in logs or outputs.
State Locking Errors
Error: Error locking state: Error acquiring the state lock

Solution: Ensure no other Terraform process is running. Use terraform force-unlock to manually unlock the state if needed. State locking prevents concurrent operations, which can lead to state corruption.
AWS Service Errors
Error: Error launching source instance: InvalidAMIID.NotFound

Solution: Verify the validity of your resource configurations, such as AMI IDs and instance types. Ensure you are referencing the correct and available resources.
Module Source Errors
Error: Failed to download module
 Solution: Check the module source URL and ensure it is accessible. The URL should point to a valid module repository, such as the Terraform Registry or a version control system.
Solution: Check the module source URL and ensure it is accessible. The URL should point to a valid module repository, such as the Terraform Registry or a version control system.
Network Configuration Errors
Error: Error creating subnet: InvalidSubnet.Range

Solution: Ensure your network configurations, like CIDR blocks, are correct and do not overlap. Properly defined network ranges are crucial for setting up a functional network infrastructure.
Resource Deletion Errors
Error: Error deleting S3 bucket: BucketNotEmpty

Solution: Empty the S3 bucket before attempting to delete it. AWS does not allow the deletion of buckets with existing objects, so ensure the bucket is empty.
Unsupported Attribute
Error: Unsupported attribute

Solution: Verify the resource or module documentation to ensure the attribute you’re using is supported. Using unsupported attributes can lead to configuration failures.
Invalid Value for Variable
Error: Invalid value for variable

Solution: Ensure the value provided for a variable is valid and meets any constraints defined in the variable block. Proper variable values are essential for successful resource creation.
Terraform Backend Errors
Error: Error configuring the backend

Solution: Verify the backend configuration in your backend.tf file. Ensure the backend service (e.g., S3 for remote state storage) is accessible and properly configured.
Invalid Data Source
Error: Invalid data source

Solution: Ensure the data source configuration is correct and the referenced data source exists. Valid data sources are crucial for retrieving accurate information.
Resource Not Found
Error: Error reading resource: NotFound

Solution: Check that the resource exists and the identifier used in the configuration is correct. Accurate identifiers ensure Terraform can manage resources correctly.
Template Render Errors
Error: Error rendering template
Solution: Ensure your template syntax is correct and that all variables used in the template are defined and accessible. Proper template rendering is essential for generating dynamic configurations.
Conclusion
Understanding these common Terraform errors and their solutions will help you troubleshoot and resolve issues effectively while running Terraform code. By following these tips, you can ensure smoother deployments and more reliable infrastructure management.
FAQs
What is Terraform?
Terraform is an open-source infrastructure as code tool that allows you to define and provision infrastructure using a declarative configuration language.
How do I initialize a Terraform project?
Use the terraform init command to initialize a Terraform project. This sets up the necessary plugins and prepares your environment for Terraform operations.
What should I do if my Terraform state file becomes corrupted?
If your state file becomes corrupted, restore it from a backup if available. Regular backups of your state file can prevent data loss and ensure smooth recovery.
How can I avoid circular dependencies in Terraform?
Avoid circular dependencies by carefully planning resource dependencies and using the depends_on attribute when necessary to explicitly define dependencies.
What are some best practices for managing Terraform configurations?
Use version control to manage your Terraform configurations, modularize your code for reusability, and regularly validate and plan your configurations to catch errors early.
Related/References
- HashiCorp Infrastructure Automation Certification: Terraform Associate
- HashiCorp Certified Terraform Associate-Step By Step Activity Guides
- Install Terraform in Linux, Mac, Windows
- Why Terraform? Not Chef, Ansible, Puppet, CloudFormation?
- Terraform Providers Overview
- Terraform Variables – Terraform Variable Types
Join FREE Class
🚀 Master Terraform & DevOps to get High-Paying Jobs! 🔥 Join our EXCLUSIVE Free class! 🚀
Get your hands dirty with lots of projects and labs based on Terraform and DevOps in our Program. Click on the below image to Register for Our FREE Class Now!







![Microsoft Agentic AI Business Solutions Architect [AB-100] | K21 Academy](https://test.k21academy.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/11/Microsoft-Agentic-AI-Business-Solutions-Architect-AB-100-Exam-Overview1.png)



