![]()
This blog post covers a brief overview of the topics covered and some common questions asked on Day 2 Live Interactive training on Microsoft Power BI Data Analyst Associate [PL-300]
This post will help you learn about Prepare data for analysis and prepare you for the certification and get a better-paid job in the field of Data Analyst.
On our Day 2 Live Session, we covered how to Get data in Power BI Clean, transform, and load data in Power BI and performed hands-on Lab 2 out of 11 hands-on Labs. We learned about how to apply various transformations and apply queries to load them to the data model and many more.
In our Day 1 session, we covered the topics on Get Started with Microsoft Data Analytics
>Power Query Editor
- Power Query Editor in Power BI Desktop allows you to shape (transform) your imported data.
- Actions such as renaming columns or tables, changing text to numbers, removing rows, setting the first row as headers, and much more can be accomplished.

Source: Microsoft
>Shape the Initial Data
Source: Microsoft
Also, Check Our blog post on Power bi GateWay Setup. Click here
>Simplify the Data Structure
- When you import data from multiple sources into Power BI Desktop, the data retains its predefined table and column names.
- You might want to change some of the names so that they are in a consistent format, easier to work with, and more meaningful to a user.
- You can use Power Query Editor in Power BI Desktop to make these name changes and simplify your data structure.
>Minimizing Errors using Power Query Editor
- When you import a table from any data source, Power BI Desktop automatically starts scanning the first 1,000 rows (default setting) and tries to detect the type of data in the columns.
- Some situations might occur where Power BI Desktop does not detect the correct data type. Where incorrect data types occur, you will experience performance issues.
- You may get a higher chance of getting data type errors while dealing with flat files, such as comma-separated values (.CSV) files and Excel workbooks (.XLSX), because of entering the data manually into the worksheets and mistakes were made.
- So the best practice is to evaluate the column data types in Power Query Editor before you load the data into a Power BI data model
Also Check: How to Create KPI in Power bi. Click here
>Profile Data in Power BI
- Profiling data means studying every detail of the data
- It can be identifying anomalies, or detecting errors.
- After examining the data, it moves forward for query statistics like row counts, maximum and minimum values, etc.
- This is the most important concept in the whole data analysis process as it allows us to shape and organize the data
- If the data is well organized we can interact with it easily
- We can make reports with fewer efforts
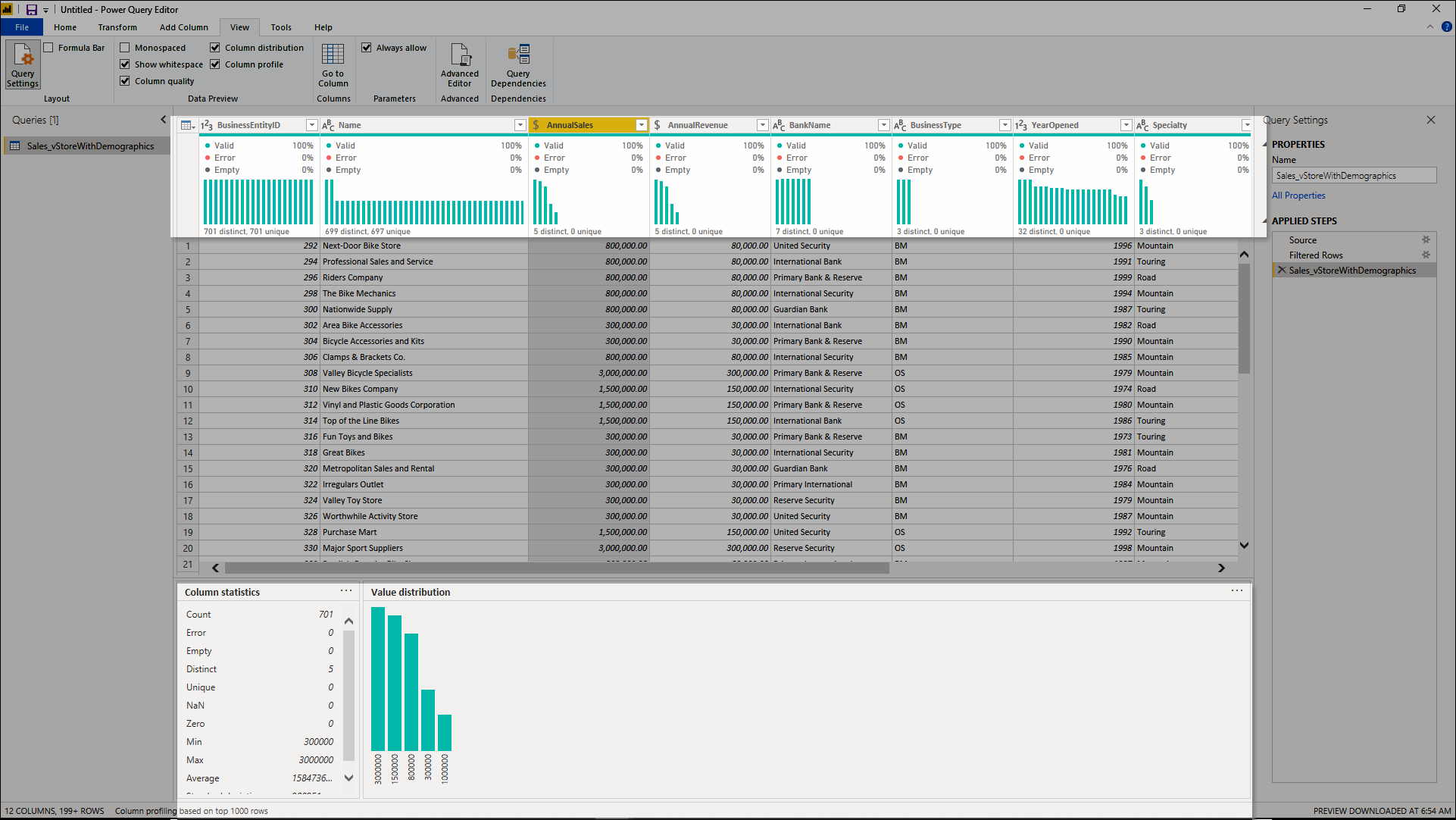
Source: Microsoft
Also, Check Our blog post on Microsoft Power bi Developer. Click here
>Combining Multiple Rows into a Single Table
- When too many tables exist, it will be difficult to navigate an overly complicated data model.
- Several tables have a similar role.
- In a table, only a column or two can fit into a different table
- You want to use several columns from different tables in a custom column.
We can join two tables together in the following ways:
Also Check: Microsoft Power bi vs SSRS, know their major differences!
FAQ Asked during the Session:
Q1: How do I prepare data for analysis in Power BI?
A: To prepare data for analysis in Power BI, you can follow these steps:
- Connect to your data source by selecting the appropriate connector in Power BI.
- Identify and understand the structure of your data.
- Clean the data by removing any duplicates, correcting errors, or handling missing values.
- Transform the data by applying filters, aggregations, calculations, or other data manipulations.
- Create relationships between tables if your data is stored in a relational format.
- Optimize the data model for performance by managing column data types, setting data categorization, and defining appropriate table relationships.
- Load the prepared data into Power BI for analysis and visualization.
Q2: How do I get data in Power BI?
A: To get data in Power BI, you can follow these steps:
- Open Power BI Desktop.
- Click on “Get Data” in the Home tab of the ribbon.
- Choose the desired data source from the available options, such as databases, files, online services, or Power Platform.
- Select the appropriate connector and provide the necessary credentials or connection details.
- Configure the data import options, including the tables, views, or queries to import.
- Apply any required transformations or filters to shape the data during the import process.
- Review and validate the imported data, and then load it into Power BI for further analysis and visualization.
Q3: How do I clean, transform, and load data in Power BI?
A: Power BI provides a variety of tools and features to clean, transform, and load data. Here’s an overview of the process:
- After connecting to your data source, you can use the Power Query Editor in Power BI Desktop to clean and transform your data.
- In the Power Query Editor, you can perform tasks such as removing columns, filtering rows, replacing values, splitting columns, merging tables, or applying advanced transformations using M or Power Query Formula Language.
- You can also apply data profiling to identify and handle issues like missing values, duplicates, or outliers.
- Once you have completed the necessary data transformations, you can click “Close & Apply” to load the transformed data into Power BI.
- Power BI will create a data model based on the loaded data, which you can then use for analysis, visualization, and report creation.
Q4:What is a Power Query?
A. Power Query is a data transformation and data preparation engine. Power Query comes with a graphical interface for getting data from sources and a Power Query Editor for applying transformations.
Source: Microsoft
Q5: Is query folding available only if you are pulling data from a single table?
Q6: How can we join two or more tables in Power BI?
Q7: What is the difference between Power BI Desktop and Power BI Service?
Power BI Service is a cloud-based service where users interact with the reports and view. The desktop application is used by Report Designers to publish the Power BI reports to the Service.
Q8: What are some of the differences in data modeling between Power BI Desktop and Power Pivot for Excel?
Q9: What is grouping in Power BI Desktop?
Q10: Is Power BI better than Excel?
Q11: Name the language that is used in the power query.
Q12: What is the Power BI Designer?
Q13:What are Data Anomalies?
A. Data anomalies are outliers within our data.
Q14: What is self-service business intelligence?
Q15:What are the data destinations for Power Queries?
Also Check: How to Create Power bi App. Click here
Q16: How can I disable the data model option in a power bi-pivot table? Also, is there any way to create dynamic formulas on a power bi-pivot table?
A. There is no way to disable the data model option in a power bi-pivot table.
Yes, we can create dynamic formulas on a pivot table. You can refer to this link to understand better.
Q17: Is there a limit on the amount you can import into Power Bi when loading data?
A. There is a 1 GB limit per dataset that is imported into Power BI unless the workspace is in a Power BI Premium capacity.
Quiz Time (Sample Exam Questions)
With our Microsoft Power BI Data Analyst Associate, we cover Over 100+ Sample questions to help you prepare for the Certification [PL-300]
Check out these Questions:
Comment your answer in the comment box.
References
- Microsoft Certified Data Analyst Associate [PL-300]: Everything You Need To Know
- Microsoft Certified Data Analyst Associate [PL-300] Step By Step Activity Guides (Hands-On Labs)
- What is Power Query | Microsoft Azure Power BI Tool
- How to Transform Data in Power BI – Clean and Load Data in Power Query
- [PL-300] Day 1 Q/A Review] Data Analytics, Prepare Data in Power BI
Next Steps to Begin with PL-300 Certification:
In our PL-300 Certification Training Program, we’ll cover 10+ Hands-On Labs. If you wish to start your journey towards becoming a Microsoft Certified: Power BI Data Analyst Associate, try our FREE CLASS.







![Microsoft Agentic AI Business Solutions Architect [AB-100] | K21 Academy](https://test.k21academy.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/11/Microsoft-Agentic-AI-Business-Solutions-Architect-AB-100-Exam-Overview1.png)


