![]()
In this video-blog, we are about to cover Microsoft Azure’s most important concepts like Azure Availability Zones, Azure Regions, Availability Set, Fault Domain, and Update Domain In Azure, and how it plays a key role in Virtual Machines.
Note: Also read our previous blog on What is Resource Group and How to Create Resource Group.
Topics covered in this blog are:
- Azure Region
- Microsoft Azure Data Center Locations
- Benefits of a Direct Connection to Azure Locations
- What is Region Pairing?
- Region Pairs
- Geographies
- Azure Availability Zone
- Azure Availability Set
- Availability Set vs Availability Zone
- When should I use an Available Zone vs Set?
- Microsoft Azure’s regions vs. Amazon Availability Zones
- Azure Fault Domains and Update Domains
- Important Notes on Availability Sets
- Frequently Asked Questions(FAQs)
The basic Architecture of the Azure can easily be understood by the following diagram

Azure Region
Azure regions are geographic locations where Microsoft Azure operates datacenters. They provide organizations with the flexibility to deploy their resources in specific regions for performance optimization, compliance, and availability purposes.
A region is a set of data centers deployed within a latency-defined perimeter and connected through a dedicated regional low-latency network.
With more global regions than any other cloud provider, Azure gives customers the flexibility to deploy applications where they need to. Azure is generally available in 60+ regions around the world and still growing.

Also read: Everything you need to know on Azure SQL Database
List of Azure regions with availability zones
Azure provides the foremost extensive global footprint of any cloud provider and is rapidly opening new regions and availability zones. the subsequent regions currently support availability zones.
| America | Europe | Middle East | Africa | Asia Pacific |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Brazil South | France Central | Qatar Central | South Africa North | Australia East |
| Canada Central | Italy North | UAE North | South Africa | Central India |
| Central US | Germany West Central | Israel Central | Japan East | |
| East US | Norway East | Korea Central | ||
| East US 2 | North Europe | Southeast Asia | ||
| South Central US | UK South | East Asia | ||
| US Gov Virginia | West Europe | China North 3 | ||
| West US 2 | Sweden Central | Australia Central | ||
| West US 3 | Switzerland North | Australia Southeast | ||
| Canada East | Poland Central |
Microsoft Azure Data Center Locations
Microsoft Azure currently has 60+ regions operative and more under development. Within each Azure region are 1 to three unique physical locations, referred to as availability zones, which provide high uptime to safeguard data and applications from data center failures.
Presently, Microsoft Azure has 126 availability zones operational and an additional 37 under development, meaning that the corporate will have a complete of 163 availability zones existing within the near-term.

Each Microsoft Azure availability zone is created from one or more data centers equipped with independent power, cooling, and networking. The physical separation of availability zones within a neighborhood protects applications and data from facility-level disruptions.
Benefits of a Direct Connection to Azure Locations
- Layer 3 connectivity between your on-premises network and therefore the Microsoft Cloud through a connectivity provider. Connectivity is from an any-to-any (IPVPN) network, a point-to-point Ethernet connection, or through a virtual cross-connection via an Ethernet exchange.
- Connectivity to Microsoft cloud services across all regions within the geopolitical region.
- Global connectivity to Microsoft Azure services across all regions with the ExpressRoute premium add-on.
- Dynamic routing between your network and Azure Microsoft via BGP.
- Built-in redundancy in every peering location for higher reliability.
- Connection uptime SLA.
- QoS support for Skype for Business.
What is Region Pairing?
Azure employs a unique feature among major cloud providers known as region pairing. This concept involves pairing two Azure regions within the same geographical area to provide geographically redundant solutions. These paired regions are interconnected with high-bandwidth, low-latency links to facilitate data replication and ensure resilience during catastrophic regional failures.
Typically, each Azure region is paired with another within the same geography or geopolitical boundary. For instance, in the United States, East US 2 (Virginia) is paired with Central US (Iowa), and East US (Virginia) is paired with West US (California). This pairing strategy ensures that in the event of a disaster recovery (DR) failover, the secondary region remains within a reasonable proximity, minimizing latency and maintaining service levels.
However, there is an exception to this general rule. Brazil South is paired with South Central US, which is outside Brazil’s geographical boundary. This pairing is an edge case and is primarily due to specific regional considerations.
By leveraging region pairing, Azure provides several advantages:
-
Geo-redundant storage services automatically replicate data between paired regions.
-
Staggered updates are rolled out across paired regions to minimize downtime and reduce the risk of simultaneous failures.
-
Prioritized recovery ensures that in the event of a catastrophic failure, at least one region in each pair is restored promptly.
It’s important to note that deploying resources in a region pair does not automatically guarantee high availability or disaster recovery. Organizations must design their solutions to utilize these pairings effectively, considering factors like latency, compliance requirements, and service availabilit
Region Pairs
- Each Azure region pairs with another region within the same geography, together making a regional pair.
- Azure serializes platform updates so only one region is updated at a time.
- Azure Regions in a Pair have direct connections that bring additional benefits to use them together.
- Each Azure Region in a pair is always located greater than 300 miles apart when possible.
- Examples of region pairs are West US paired with East US, South-East Asia paired with East Asia.

Also check: Steps to register Azure Free Account
Geographies
Geography is a discrete market, typically containing two or more regions, that preserves data residency and compliance boundaries.
It allows customers with specific data-residency and compliance needs to keep their data and applications close. However, they are fault-tolerant to withstand complete region failure through their connection to our dedicated high-capacity networking infrastructure.
To know more about the Geography locations refer here

Also check: Step by Step instructions to install Azure Powershell module
Azure Availability Zone
- Azure Availability Zones is a high-availability offering that protects your applications and data from datacenter failures.
- These are unique physical locations within an Azure region. Each zone is made up of one or more data centers equipped with independent power, cooling, and networking.
- The physical separation of Availability Zones within a region protects applications and data from datacenter failures.
- Zone-redundant services replicate your applications and data across Azure Zones to protect from single-points-of-failure.
- Not every region has support for Availability Zone Azure. The examples of Availability Zones are Central US, East US 2, West US 2, West Europe, France Central, North Europe & Southeast Asia
- With Availability Zones, Azure offers industry best 99.99% VM uptime SLA(Service Level Agreement)

To achieve comprehensive business continuity on Azure, build your application architecture using the combination of Azure Zones with Azure region pairs.

Azure Availability Set
- An Availability Set is a logical grouping capability for isolating VM resources from each other when they’re deployed.
- By deploying your VMs across multiple hardware nodes Azure ensures that if hardware or software failure happens within Azure, only a sub-set of your virtual machines is impacted and your overall solution is safe and in working condition.
- It provides redundancy for your virtual machines.
- An Availability set spreads your virtual machines across multiple fault domains and update domains.
- If you want to leverage Microsoft’s 99.95% SLA from Microsoft you must place your VMs inside availability set except your VMs are having premium storage.
An Update Domain and Fault Domain is assigned to each VM in Availability Set by Azure platform.
Availability Set vs Availability Zone
Availability Sets takes the virtual machine and configures multiple copies of it. Each copy is isolated within a separate physical server, compute rack, storage units and network switches within one datacentre within an Azure Region.
When you create your virtual machine you’ll be able to specify the provision Set, you can’t change it or move it in or out of an Availability Set after creation. If you wanted to create changes you’d start again and recreate the virtual machine. And Availability Sets only apply to virtual machines, they can’t be used for the other kind of resources within Azure.
Using an Availability Set takes your acceptable downtime to around 21.6 minutes a month. Which could be a vast improvement over the one virtual machine deployment.
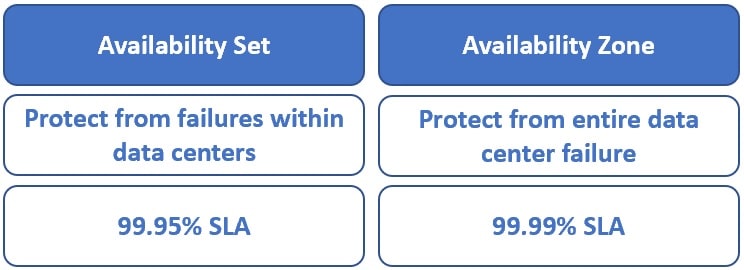
The next level of availability for your virtual machines within Azure is Availability Zones. With Availability Zones utilised your acceptable downtime a month moves to but 4.32 minutes as you’ve got a 99.99% SLA.
| Feature | Availability Set | Availability Zone |
|---|---|---|
| Scope of Redundancy | Single data center | Multiple isolated data centers within an Azure region |
| Fault Isolation | Isolated within fault domains (racks) and update domains (maintenance groups) | Isolated across entire data centers with independent power, cooling, and networking |
| Protection Level | Protects against localized hardware or software failures | Protects against entire data center failures |
| Service-Level Agreement (SLA) | 99.95% for VMs deployed in an Availability Set | 99.99% for VMs deployed across multiple Availability Zones |
| Physical Separation | Not physically separated; all VMs reside within the same data center | Physically separated; each zone is a separate data center within the region |
| Update Domain & Fault Domain | VMs are distributed across multiple update and fault domains to minimize impact during maintenance or failures | Each zone acts as a separate fault and update domain |
| Cost | No additional cost for using Availability Sets | No additional cost for using Availability Zones |
| Applicable Resources | Virtual Machines only | Virtual Machines and other Azure resources |
| Use Cases | Suitable for applications that can tolerate brief downtime and require high availability within a single data center | Ideal for mission-critical applications requiring high availability and disaster recovery across data centers |
With Availability Zones, you’re setting out to use zone-aware services. Your workload is opened up across the various zones that compose an Azure region. An Azure region is formed from multiple datacentres and every zone is formed from one or more datacentres. Each datacentre is provided with independent power, cooling and networking.
When should I use an Available Zone vs Set?
When building your workload in Azure, it’s important to carefully consider how you create availability for your virtual machine infrastructure. There are several factors to keep in mind when choosing whether to use Availability Sets or Availability Zones.
Cost
Using an Availability Zone incurs additional bandwidth costs for data moving in and out of the zone. Although this cost is quite minimal — approximately 1 pence per GB — it can add up quickly for workloads with high data transfer volumes.
Storage
Availability Zones support managed disks directly, whereas Availability Sets do not. This does not mean that managed disks attached to VMs in Availability Sets are less available. They are still provisioned to be isolated from single points of failure. However, with Availability Zones, copies of managed disks are replicated in each zone, providing higher redundancy.
Availability
Availability Sets and Availability Zones are different Azure services and have different Service Level Agreements (SLAs). The SLA specifies the guaranteed uptime percentage for the compute resources or services running your workloads. It does not guarantee uptime for your entire application or workload but focuses on the underlying Azure infrastructure.
-
Availability Sets guarantee a 99.95% uptime.
-
Availability Zones guarantee a 99.99% uptime.
Although this difference may seem small, on paper it translates to roughly 5 hours of cumulative downtime per year with Availability Sets versus under 1 hour per year with Availability Zones.
Microsoft Azure’s regions vs. Amazon Availability Zones
Azure’s Region Pairing:
Azure employs a unique feature among major cloud providers known as region pairing. This concept involves pairing two Azure regions within the same geographical area to provide geographically redundant solutions. These paired regions are interconnected with high-bandwidth, low-latency links to facilitate data replication and ensure resilience during catastrophic regional failures.
Typically, each Azure region is paired with another within the same geography or geopolitical boundary. For instance, in the United States, East US 2 (Virginia) is paired with Central US (Iowa), and East US (Virginia) is paired with West US (California). This pairing strategy ensures that in the event of a disaster recovery (DR) failover, the secondary region remains within a reasonable proximity, minimizing latency and maintaining service levels.
However, there is an exception to this general rule. Brazil South is paired with South Central US, which is outside Brazil’s geographical boundary. This pairing is an edge case and is primarily due to specific regional considerations.
AWS’s Availability Zones:
Amazon Web Services (AWS) utilizes Availability Zones as the primary method for achieving high availability within a region. An Availability Zone is a physically separate location within an AWS region, each with its own independent power, cooling, and networking. These zones are interconnected with low-latency links, allowing applications to be distributed across multiple zones to achieve fault tolerance and low-latency performance.
AWS regions typically consist of at least three Availability Zones, providing customers with the flexibility to architect applications that can withstand failures of an entire data center. This design enhances the resilience and availability of applications deployed within AWS.
Comparison:
| Feature | Azure Region Pairing | AWS Availability Zones |
|---|---|---|
| Scope of Redundancy | Region-level redundancy | Data center-level redundancy within a region |
| Geographical Separation | Regions are typically separated by at least 300 miles | Availability Zones are physically separated within a region, typically within 60 miles (100 km) of each other |
| Interconnectivity | High-bandwidth, low-latency links between paired regions | Low-latency links between Availability Zones within a region |
| Primary Use Case | Disaster recovery and geo-redundancy | High availability and fault tolerance within a region |
| Latency Considerations | Potentially higher latency between paired regions | Low latency between Availability Zones within the same region |
| Cost Implications | Data transfer between paired regions may incur additional costs | Data transfer between Availability Zones within the same region is typically free |
| Service Availability | Not all Azure regions support Availability Zones | Each AWS region has multiple Availability Zones |
Azure Fault Domains and Update Domains
Fault Domains
- Fault domains are groups of virtual machines that share a common power source and network switch.
-
Each fault domain consists of one or more racks in a data centre.
- If a fault domain experiences hardware failure, all resources within it can become unavailable.
- Distribute VMs across fault domains to reduce risk of simultaneous failures (e.g., one web server in each fault domain).

Update Domains
- Update domains are logical groups used to sequence VM updates and reboots.
- During planned maintenance, only one update domain is rebooted at a time to minimize downtime.
-
Azure assigns VMs to update domains automatically within an availability set.
- Azure Resource Manager (ARM) supports up to 3 fault domains and 20 update domains.

Check Out: What is Azure Virtual Machine Scale Set?
- In the Azure Service Management (ASM) portal, we have two Fault domains and 5 update domains.
- In the Azure Resource Manager(ARM) portal, we have three Fault domains and 5 update domains but we can upgrade our update domains from 5 to 20.
- VMs are assigned sequentially in the update domains and fault domains.
Check Out: Azure load balancer vs Application Gateway: know their major differences!SLA(Service Level Agreement) for VM:
Important Notes on Availability Sets
-
Virtual machines must be created within the same resource group and assigned to an availability set during creation.
-
A VM can only belong to one availability set.
-
Azure guarantees 99.95% uptime for VMs with two or more instances in the same availability set.
-
Single-instance VMs with premium storage have a 99.9% uptime SLA.
- For all Virtual Machines that have two or more instances deployed in the same Availability Set, Azure guarantees you will have Virtual Machine Connectivity to at least one instance at least 99.95% of the time.
- For any Single Instance Virtual Machine using premium storage for all disks, Azure guarantees you will have Virtual Machine Connectivity of at least 99.9%.
 Also Read: Our previous blog post on Azure Blob Storage. Click hereHope the blog will help you in understanding the concepts of Region, Availability Zone, Availability Set, Fault Domain, and Update Domain, and how it plays a key role in Virtual Machines. Now it’s your turn to post your doubts in the comment section.
Also Read: Our previous blog post on Azure Blob Storage. Click hereHope the blog will help you in understanding the concepts of Region, Availability Zone, Availability Set, Fault Domain, and Update Domain, and how it plays a key role in Virtual Machines. Now it’s your turn to post your doubts in the comment section.
Frequently Asked Questions(FAQs)
Q1. What is difference between update domain and fault domain in Azure?
The difference between update domain and fault domain are:
- Update domains are used to isolate resources for maintenance and updates, while fault domains are used to isolate resources from hardware and software failures
- All of the resources in an update domain must be capable of being updated or rebooted simultaneously by Azure. However, fault domains must not be so big that all of the resources inside it become unavailable in the event of a failure; rather, they must be big enough to isolate resources from failures.
Q2. What is the difference between availability zone and fault domain in Azure?
The main difference between fault domain and update domain is availability zone is a physical location, while a fault domain is a logical grouping of hardware
Q3. What are regions in Azure?
Azure regions refer to the geographic areas where Microsoft Azure has deployed its data centers. Each region is a separate geographic location where Azure resources, such as virtual machines, storage accounts, and databases, can be provisioned. Regions are strategically located around the world to ensure global coverage and support for customers' cloud computing needs.
It's worth noting that Microsoft continues to expand its Azure footprint by adding new regions and availability zones over time to cater to growing customer needs and improve service coverage
Q4. What is the use of Azure Regions?
Azure regions serve multiple purposes and provide several benefits for organizations using Microsoft Azure. Here's an overview of the uses and advantages of Azure regions:
- Geographic Distribution
- Data Residency and Compliance
- Disaster Recovery and Business Continuity
- High Availability and Fault Tolerance
- Service Selection and Feature Availability
- Scalability and Load Balancing
Q5. What is the purpose of Availability Zones in Azure?
The purpose of Availability Zones in Azure is to enhance the reliability and resiliency of business-critical workloads by providing redundancy and isolation within an Azure region. Availability Zones are physically separate zones within an Azure region, each having its own power source, network, and cooling infrastructure
- Region, Availability Domain (AD), Fault Domain (FD) & Realm in Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI)
- [AZ-104] Microsoft Azure Administrator Certification Exam: Everything You Need To Know
- Manage the availability of Windows virtual machines in Azure
- Exam AZ-305: Azure Solutions Architect Expert Certification
- ARM Template: Azure Resource Manager Template Tutorial
- Virtual Machine Scale Set (VMSS) In Microsoft Azure
- Azure Networking : Brief Introduction of Azure Virtual Network
- Azure Load Balancer : Azure Front Door vs. Application Gateway
Next Task For YouBegin your journey toward Mastering Azure Cloud and landing high-paying jobs. Just click on the register now button on the below image to register for a Free Class on Mastering Azure Cloud: How to Build In-Demand Skills and Land High-Paying Jobs. This class will help you understand better, so you can choose the right career path and get a higher paying job.
| Feature | Azure Region Pairing | AWS Availability Zones |
|---|---|---|
| Scope of Redundancy | Region-level redundancy |






![Microsoft Agentic AI Business Solutions Architect [AB-100] | K21 Academy](https://test.k21academy.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/11/Microsoft-Agentic-AI-Business-Solutions-Architect-AB-100-Exam-Overview1.png)



