![]()
If you look around today, almost everything we use—whether it’s Netflix, online banking, food delivery apps, or even college learning portals—is powered by the cloud. Instead of companies buying and maintaining heavy servers, they now rely on platforms like Amazon Web Services (AWS) and Microsoft Azure. The cloud has simply made it easier, faster, and cheaper to build and run applications.
Now, here’s the thing: learning about the cloud from books or tutorials is one step, but if you really want to understand how it works, you need to build projects. Just like you can’t learn driving by reading a manual, you can’t learn cloud computing without some hands-on practice.
For students, freshers, or anyone looking to break into cloud engineering, projects are your best friends. They help you see how services connect, how to fix issues when things don’t work, and how to design systems that are reliable and scalable. The good part is, you don’t have to start big. Even a simple project like setting up a 3-tier web app can teach you networking, databases, and security basics.
In this blog, I’ll share Top AWS & Azure Cloud Projects in 2026 (5 on AWS and 5 on Azure) that cover everything from basic architectures to advanced setups like Kubernetes, identity management, VPNs, and disaster recovery. These projects are not just for learning—they’re the same kind of work done in real companies. If you stick with them, you’ll build confidence, a stronger resume, and solid talking points for your interviews.
Topics to be covered
AWS Projects
- Deploy 3-Tier Architecture (Web, App, Database)
- DevOps: End-to-End CI/CD Pipeline
- Migration: Monolithic App to Microservices
- AWS Backup and Recovery: End-to-End Data Integrity
- Deploy Web App on AWS ECS with GitHub Actions
Azure Projects
- Deployment of 3-Tier Architecture in Azure
- Deploying a Multi-Container Application to AKS
- Migration of Resources from On-Premise to Azure
- Entra ID Synchronization with On-Premise Active Directory
- Site-to-Site VPN Connection using Azure Portal
Top 5 AWS Cloud Projects 2026
Project 1: Deploy 3-Tier Architecture (Web, App, Database)
A 3-Tier Architecture is one of the most popular cloud application designs because it separates applications into three logical layers: the Web Layer (user interface), the Application Layer (business logic), and the Database Layer (data storage and management). Each tier has its own responsibilities and can be managed, scaled, and secured independently. By deploying this on AWS, we not only make the application more resilient and fault-tolerant, but we also ensure it can handle millions of users with smooth performance. This project introduces the foundation of modern application design, making it essential for any aspiring cloud engineer.
Key Features
- Separation of Concerns – Each tier performs a distinct role, making the system modular and easy to manage.
- Independent Scaling – If the app tier faces heavy traffic, only that layer can be scaled without affecting the others.
- Security Layers – Sensitive data is isolated in the database layer with private subnets and encryption.
- Load Balancing – Ensures high availability by spreading incoming requests across multiple servers.
- Fault Tolerance – Even if one component fails, the application continues to function through redundancy.
Technologies Used
- Amazon EC2 – Hosts the web and application servers, providing flexible compute power.
- Amazon RDS – Managed relational database service that handles backups, patches, and scaling automatically.
- Elastic Load Balancer (ELB) – Distributes incoming requests evenly across multiple web/app instances.
- Amazon VPC – Provides secure networking, subnets, and routing between tiers.
- AWS IAM – Manages roles and permissions to ensure only authorized access to resources.
Skills to Develop
- Cloud Architecture Design – Learn how to design modular systems that can be scaled independently.
- Networking Basics – Configure subnets, security groups, and firewalls in a VPC.
- Database Management – Understand how to deploy, secure, and scale relational databases.
- Load Balancing & Scaling – Implement auto-scaling policies to handle fluctuating workloads.
Advantages
- High scalability and performance.
- Easier maintenance since each layer can be updated independently.
- Enhanced security by isolating sensitive data.
- Supports enterprise-grade applications and traffic loads.
Real-World Use Cases
- Banking applications where user interfaces, transaction logic, and secure databases must remain separate.
- E-commerce platforms handling user browsing, cart management, and order data across different layers.
For more info learn from here:- Click Here
Project 2: DevOps: End-to-End CI/CD Pipeline
The CI/CD Pipeline is the backbone of modern software delivery. Instead of manually writing code, testing it, and deploying it, everything is automated. Developers push code to GitHub, automated workflows kick in, the code is built, tested, and deployed without human intervention. This project shows how to integrate Continuous Integration (CI) and Continuous Delivery (CD) using AWS services, helping teams deliver software faster, more reliably, and with fewer bugs.
Key Features
- Automated Code Build – Every code commit automatically triggers a build process.
- Continuous Testing – Automated testing ensures issues are detected early in development.
- Deployment Automation – The latest stable code is deployed automatically to staging or production.
- Rollback Support – Quickly revert to a previous version if deployment fails.
- Team Collaboration – Transparent workflows help developers, testers, and operations teams work together.
Technologies Used
- GitHub/GitLab – Source code repositories with version control.
- AWS CodePipeline – Orchestrates the entire CI/CD workflow.
- AWS CodeBuild – Compiles source code, runs tests, and produces ready-to-deploy artifacts.
- AWS CodeDeploy – Deploys applications to EC2, ECS, or Lambda automatically.
- Amazon CloudWatch – Monitors pipeline activities and alerts on failures.
Skills to Develop
- Pipeline Automation – Learn to connect code repositories to deployment environments.
- Test Automation – Configure tests to run automatically on every code push.
- Source Control – Master Git workflows for collaborative development.
- Deployment Strategies – Understand blue/green, rolling, and canary deployments.
Advantages
- Faster release cycles with fewer bugs.
- Reduces human error in deployments.
- Improves collaboration and visibility.
- Enables continuous innovation and delivery.
Real-World Use Cases
- Startups than need to deliver features weekly with minimal downtime.
- Enterprises that maintain multiple versions of the same app across regions.
For more info learn from here:- Click Here
Project 3: Migration: Monolithic App to Microservices
Traditional applications are often monolithic—all features and logic are tightly coupled into one big unit. This makes them difficult to scale, update, or debug. By migrating to microservices, each feature (authentication, cart, payments, notifications) becomes a standalone service that runs independently. In AWS, these services are deployed in containers, communicate via APIs, and can scale on their own. This project gives hands-on experience in modernizing legacy apps for cloud-native environments.
For more info learn from here:- Click Here
Key Features
- Service Decomposition – Large applications are broken into smaller, independent services.
- Containerization – Docker is used to package services for portability and consistency.
- API Communication – REST or gRPC APIs allow services to talk to each other securely.
- Scalable Deployment – ECS/EKS runs microservices and scales them individually.
- Fault Isolation – A failure in one service does not bring down the entire system.
Technologies Used
- Docker – Packages services into portable containers.
- Amazon ECS / EKS – Runs and manages containerized applications at scale.
- API Gateway – Provides secure entry points for microservice communication.
- AWS IAM & VPC – Controls security, roles, and network isolation.
- Amazon CloudWatch – Tracks microservice performance and logs.
Skills to Develop
- Microservices Design – Learn how to identify boundaries and responsibilities for services.
- Container Management – Build, run, and deploy Docker containers in the cloud.
- Security Best Practices – Configure IAM and VPC for secure communication.
- Orchestration – Manage complex deployments using ECS or Kubernetes.
Advantages
- Independent scaling for high-demand services.
- Easier upgrades and faster delivery cycles.
- Improved resilience due to service isolation.
- Better team productivity since teams can own individual services.
Real-World Use Cases
- Netflix runs hundreds of microservices for content delivery.
- Amazon handles payments, product catalog, and orders as independent services.
Project 4: AWS Backup and Recovery: End-to-End Data Integrity
In today’s digital world, data is the most critical asset. Losing it due to failures, disasters, or human error can be devastating. This project focuses on creating a comprehensive backup and recovery plan using AWS. With AWS Backup and other services, businesses can automate backups, ensure compliance, and quickly recover from data loss, thus ensuring business continuity.
Key Features
- Automated Backup Plans – Create scheduled policies to back up resources.
- On-Demand Backup – Perform manual backups whenever needed.
- Cross-Region Backup – Store copies in other regions for disaster recovery.
- Compliance Monitoring – Use AWS Backup Audit Manager to ensure rules are followed.
- Fast Recovery – Restore entire systems or databases with minimal downtime.
Technologies Used
- AWS Backup – Centralized backup service for AWS workloads.
- Amazon RDS Snapshots – Automated database backups and restores.
- Amazon EBS Snapshots – Block-level storage backups for EC2 volumes.
- CloudEndure Disaster Recovery – Provides near-zero downtime during disasters.
- AWS Backup Audit Manager – Monitors compliance and backup activities.
Skills to Develop
- Disaster Recovery Planning – Design strategies to protect critical workloads.
- Backup Automation – Learn to configure policies for automatic backups.
- Compliance & Security – Understand auditing and reporting for regulations.
- Recovery Techniques – Restore environments quickly with minimal loss.
Advantages
- Protects against accidental data loss.
- Ensures businesses can continue running during disasters.
- Meets government and industry compliance.
- Saves time with automation and reduces human dependency.
Real-World Use Cases
- Hospitals are backing up patient data for HIPAA compliance.
- Financial services secure transaction data with daily backups.
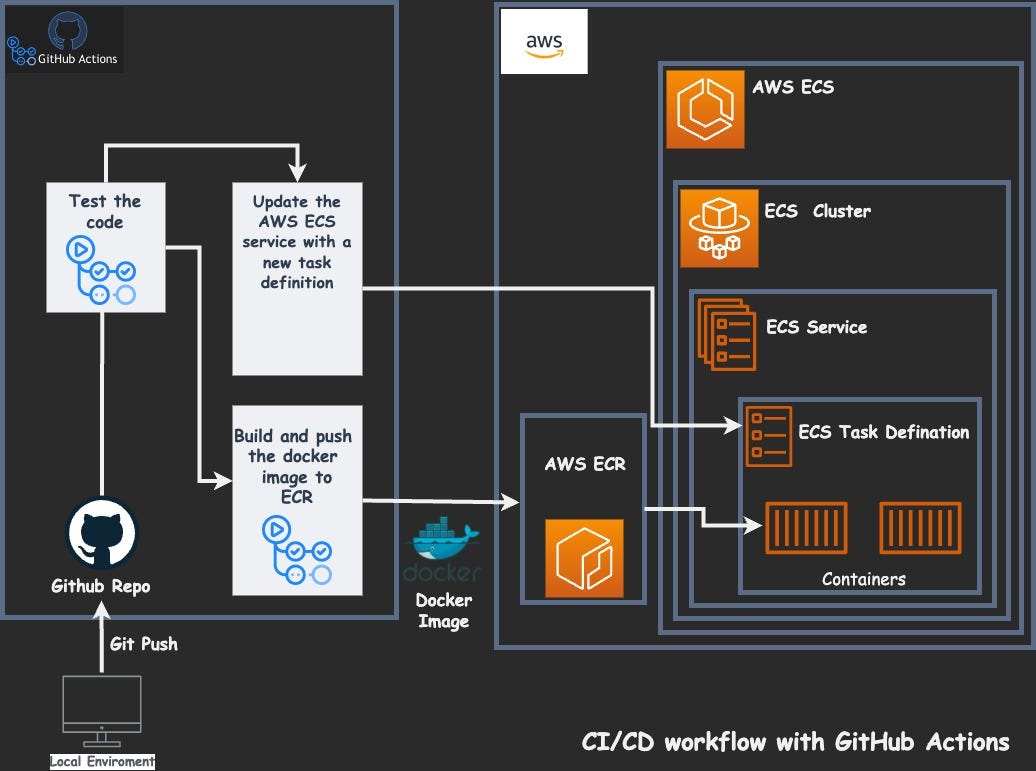
Project 5: Deploy Web App on AWS ECS with GitHub Actions
This project involves deploying a web application on AWS Elastic Container Service (ECS) using GitHub Actions for CI/CD. You learn how to automate the deployment process, integrating GitHub for source control and using ECS for scalable application hosting.
Key Features
- Source Control Integration – GitHub hosts the codebase and manages commits.
- Containerization – Docker images package the application consistently.
- Automated CI/CD – GitHub Actions automates testing and deployment.
- Scalable Hosting – ECS automatically adjusts to handle traffic.
- Zero-Downtime Updates – Rolling updates keep the app online during changes.
Technologies Used
- Docker – Builds and packages applications for portability.
- Amazon ECS – Runs and manages Docker containers in the cloud.
- AWS Fargate – Serverless compute engine for running containers without managing servers.
- Amazon ECR – Stores and manages Docker images securely.
- GitHub Actions – Automates the entire CI/CD pipeline.
- Elastic Load Balancer – Ensures application requests are evenly distributed.
Skills to Develop
- Containerization – Learn how to package applications using Docker.
- CI/CD Automation – Gain expertise in building automated workflows.
- Cloud Scaling – Understand ECS clusters, tasks, and services.
- Monitoring & Troubleshooting – Track deployments and fix issues using logs.
Advantages
- Faster deployments with less human effort.
- Consistent environments across development and production.
- High availability with automatic scaling.
- Cost efficiency since resources scale only when needed.
Real-World Use Cases
- Startups using containers to quickly ship new features.
- Enterprises automating deployments for mission-critical web apps.
For more projects refer this blog:- click here
Top 5 Azure Cloud Projects in 2026
Project 1: Deployment of 3-Tier Architecture in Azure
A 3-tier architecture divides an application into three parts: presentation, application, and data layers. This ensures modularity, scalability, and better security. In Azure, this architecture can be deployed using a combination of Azure services for each layer. The web tier manages user interaction, the app tier handles business logic, and the data tier stores and processes information. By setting up load balancers across tiers, the system becomes fault-tolerant and highly available.
Key Features
- Separation of Concerns – Each tier works independently, making management easier.
- Scalability – App and data tiers can be scaled as per demand.
- Load Balancing – Ensures equal traffic distribution and prevents overload.
- Security – Sensitive data is isolated in the database tier within private networks.
- Flexibility – Each tier can use different technologies best suited to its function.
Technologies Used
- Azure Virtual Machines – For hosting the web and application layers.
- Azure Load Balancer – To distribute incoming traffic across multiple VMs.
- Azure SQL Database – Manages and stores structured application data securely.
- Azure Virtual Network (VNet) – Provides secure communication between tiers.
Skills to Develop
- Infrastructure Setup – Learn how to build secure, isolated environments in Azure.
- Traffic Management – Configure load balancers for efficient routing.
- Database Administration – Practice managing data in Azure SQL Database.
- Application Deployment – Host and manage apps across different layers.
Advantages
- Better system organization with clear responsibility division.
- High availability and reliability due to redundancy and load balancing.
- Improved security by isolating data storage from external access.
- Easy maintenance, as each tier can be updated independently.
Real-World Use Cases
- Banking applications handling sensitive financial data.
- E-commerce platforms manage product catalogs, carts, and user accounts.
- Healthcare systems manage patient records securely.
Project 2: Deploying a Multi-Container Application to AKS
A multi-container application allows multiple services (like front-end, back-end, and database) to run together, each in its own container. With Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS), you can orchestrate and manage these containers efficiently. This project involves building a CI/CD pipeline to automate the deployment of a web application, hosting it in AKS, and connecting it with Azure SQL Database for data storage.
Key Features
- Containerization – Each service is isolated for better reliability.
- Orchestration – AKS ensures smooth scaling and container management.
- Automated Deployment – CI/CD pipelines streamline the release process.
- High Availability – Applications remain functional even if a node fails.
- Resource Optimization – Containers use fewer resources compared to VMs.
Technologies Used
- Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS) – For orchestrating containerized applications.
- Azure Container Registry (ACR) – Stores container images securely.
- Azure SQL Database – Provides relational data management.
- GitHub Actions / Azure DevOps Pipelines – Automates application deployment.
Skills to Develop
- Container Management – Learn Docker and containerized app development.
- Kubernetes Operations – Understand scaling, pod management, and services.
- CI/CD Automation – Build automated pipelines for deployments.
- Cloud-Native Design – Create applications designed for scalability.
Advantages
- Faster deployments with minimal downtime.
- Easier maintenance through modular container design.
- Enhanced fault tolerance with distributed containers.
- Cost savings by utilizing containers over heavy virtual machines.
Real-World Use Cases
- Social media platforms with microservices like chat, posts, and notifications.
- Food delivery apps combine user management, order tracking, and payments.
- SaaS products offering modular services to customers.
Project 3: Migration of Resources from On-Premise to Azure
Many organizations are moving their workloads from on-premises data centers to the cloud. This project focuses on migrating servers, and applications into Azure. The process involves setting up Azure Storage Accounts, Recovery Services Vault, and using Azure Migrate tools to lift and shift workloads. By doing so, businesses gain flexibility, scalability, and cost efficiency without worrying about physical hardware maintenance.
Key Features
- Seamless Migration – Move existing workloads without major changes.
- Business Continuity – Applications remain available during migration.
- Scalability – Quickly scale workloads as business needs change.
- Security – Built-in encryption and compliance features in Azure.
- Cost Optimization – Pay only for resources consumed.
Technologies Used
- Azure Migrate – Assesses and migrates on-premises resources.
- Azure Storage Account – Stores migration data securely.
- Azure Virtual Machines – Hosts migrated servers and workloads.
- Recovery Services Vault – Ensures backup and disaster recovery.
Skills to Develop
- Cloud Migration Planning – Learn strategies for smooth migrations.
- Data Security – Implement backup and encryption measures.
- Server Management – Handle VM deployment and configuration in Azure.
- Cost Management – Optimize resource usage after migration.
Advantages
- Reduces dependency on physical servers.
- Improves performance by leveraging Azure infrastructure.
- Enables remote accessibility for global teams.
- Provides disaster recovery and backup features.
Real-World Use Cases
- Enterprises are shifting from data centers to Azure for cost savings.
- Retail companies are moving seasonal workloads to Azure for flexibility.
- Educational institutions hosting online learning platforms in Azure.
For more projects refer this blog:- click here
Project 4: Entra ID (Azure Active Directory) Synchronization with on-premises Active Directory using Entra Connect (AD Connect)
Identity management is crucial in organizations with both on-premises and cloud resources. This project integrates the local Active Directory with Microsoft Entra ID (previously Azure AD). With Entra Connect, user accounts, groups, and policies are synchronized between environments. This ensures employees can use the same credentials for on-premises and cloud applications, enabling a seamless single sign-on (SSO) experience.
Key Features
- Identity Synchronization – Keeps users consistent across cloud and local AD.
- Single Sign-On (SSO) – Users access multiple services with one login.
- Hybrid Identity – Supports both on-premises and cloud apps.
- Automatic Updates – Changes in local AD are reflected in Entra ID.
- Enhanced Security – Reduces risks of identity mismanagement.
Technologies Used
- Microsoft Entra ID (Azure AD) – Cloud-based identity management.
- Active Directory (On-Premises) – Local user and group management.
- Entra Connect(Azure AD Connect) – Synchronization tool for both systems.
- Azure Monitor – Tracks sync health and errors.
Skills to Develop
- Identity and Access Management – Learn authentication and authorization basics.
- Directory Synchronization – Understand AD-Cloud sync mechanisms.
- SSO Configuration – Enable unified access to apps.
- Troubleshooting – Manage sync issues and replication errors.
Advantages
- Simplifies user account management across environments.
- Improves employee productivity through SSO.
- Enhances security by reducing multiple password risks.
- Provides centralized identity governance.
Real-World Use Cases
- Enterprises managing both on-premises and cloud-based apps.
- Universities are synchronizing student accounts for online learning platforms.
- Healthcare organizations ensure secure identity access for staff.
Project 5: Site-to-Site VPN Connection using Azure Portal
A Site-to-Site VPN connects an on-premises network with an Azure Virtual Network (VNet) using an encrypted IPsec tunnel. This project establishes a secure bridge between the cloud and the local data center. Setting up an Azure VPN Gateway and Local Network Gateway allows seamless communication, enabling workloads to operate as if they were in the same network.
 Key Features
Key Features
- Secure Communication – Encrypts traffic between on-premises and Azure.
- Extended Network – Combines cloud and on-premises into one network.
- Scalability – Supports multiple branch office connections.
- Redundancy – Ensures availability even if one tunnel fails.
- Centralized Control – Manage connections from the Azure Portal.
Technologies Used
- Azure Virtual Network (VNet) – Defines cloud-side network.
- Azure VPN Gateway – Acts as a cloud endpoint for VPN connections.
- Local Network Gateway – Represents the on-premises VPN device.
- IPsec/IKE Protocols – Encrypt data transmission securely.
Skills to Develop
- Networking Basics – Learn subnets, routing, and gateways.
- VPN Configuration – Gain expertise in setting up tunnels.
- Security Management – Handle encryption and access control.
- Hybrid Connectivity – Connect cloud with on-premises systems.
Advantages
- Provides secure remote access to Azure resources.
- Eliminates the need for costly dedicated leased lines.
- Enables hybrid workloads between cloud and local servers.
- Ensures compliance with security regulations.
Real-World Use Cases
- Enterprises connecting multiple office locations with Azure.
- IT companies enabling secure developer access to cloud servers.
- Government agencies are securing communication with cloud-hosted data.
For more projects refer this blog:- click here
Key Takeaways from These AWS & Azure Projects
- Strong Foundation in Cloud Architecture – You’ll learn how to design scalable and secure environments using AWS and Azure services.
- Hands-on DevOps Exposure – CI/CD pipelines, container orchestration, and automated deployments will prepare you for DevOps roles.
- Migration & Hybrid Cloud Skills – You’ll understand how to move on-premises workloads to the cloud and connect hybrid systems securely.
- Security & Identity Management – Projects like Entra ID sync and IAM configurations help you build enterprise-grade security skills.
- Practical Real-World Relevance – These aren’t just academic exercises; they reflect actual use cases in industries like finance, healthcare, e-commerce, and IT services.
Conclusion
Cloud computing is not just another “tech trend”—it’s where the future of IT, software development, and even business operations is headed. Whether you choose AWS or Azure, these platforms are everywhere, and skilled professionals are always in demand.
The Top AWS & Azure Cloud Projects in 2026 we went through in this blog are more than just exercises. They’re stepping stones. Each project builds a layer of understanding: from simple app deployments to secure networking, automation, identity management, and hybrid connections.
If you’re a student, think of them as mini-internships you can do on your own. If you’re a fresher preparing for interviews, these projects can help you answer scenario-based questions with confidence. And if you’re already working in tech but want to move into the cloud space, these projects can give you the portfolio you need.
So, don’t just stop at reading—open your AWS or Azure free account, pick one project, and actually try it. You’ll run into issues, yes, but solving them is where the real learning happens. Every project you finish will make you a bit more “cloud-ready.” And who knows? The same skills you learn here might one day be the reason you crack an interview at your dream company.
FAQ’s:-
A: Start small. Don’t jump directly into Kubernetes or VPNs. Begin with a 3-Tier Architecture project because it introduces you to the basics: web servers, databases, and networking. Once you’re comfortable, move step by step to more complex projects like CI/CD pipelines or container deployments.
A: Not necessarily. Both AWS and Azure provide free tiers for students and beginners. You’ll get limited hours of compute, some storage, and basic services at no cost. Just remember to shut down resources after you’re done with a project—otherwise, you may get charged.
A: Yes—absolutely. Interviewers often ask practical, scenario-based questions like “How would you design a fault-tolerant system?” or “How do you secure communication between services?” If you’ve actually built these projects, you can give real, confident answers. Plus, you’ll have troubleshooting experience, which is even more valuable.
A: It depends on your goals. If you want to work in startups or global companies, AWS has a bigger market share. If you’re aiming for roles in enterprises that use Microsoft technologies, Azure is a great choice. Honestly, learning both gives you a big advantage because many companies use a multi-cloud strategy.
A: Most beginners try to learn everything at once and get overwhelmed. The best way is to focus on one project at a time. Finish it, note down what you learned, and then move on. Cloud is huge—you don’t need to know it all on day one. Q1. I’m a beginner with no cloud experience. Where should I start?
Q2. Do I need to pay to do these projects on AWS or Azure?
Q3. Will these projects help me in cloud job interviews?
Q4. Which is better for my career—AWS or Azure?
Q5. What’s the biggest mistake beginners make when learning cloud?
Next Task For You
Begin your journey toward Mastering Azure Cloud and landing high-paying jobs. Just click on the register now button on the below image to register for a Free Class on Mastering Azure Cloud: How to Build In-Demand Skills and Land High-Paying Jobs. This class will help you understand better, so you can choose the right career path and get a higher paying job.


















![Microsoft Agentic AI Business Solutions Architect [AB-100] | K21 Academy](https://test.k21academy.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/11/Microsoft-Agentic-AI-Business-Solutions-Architect-AB-100-Exam-Overview1.png)



