![]()
Data engineering is the backbone of modern businesses, ensuring that massive volumes of raw data are collected, transformed, and delivered efficiently for analytics and decision-making. With the rapid rise of AI, cloud platforms, and real-time analytics, the demand for reliable and scalable 15 Best Data Engineering Tools for 2025 has never been higher.
The digital world is running on data. Every click, purchase, or interaction generates a data point. By 2025, enterprises are processing over 180 zettabytes of data globally (IDC). Handling this scale requires more than just coding—it demands powerful data engineering tools that automate ingestion, transformation, and delivery.
In this guide, we present the 15 best data engineering tools for 2025, categorized by ETL, orchestration, warehouses, and streaming engines. Whether you are a student, professional, or enterprise CTO, this list will help you make the right choice.
Topics to Be Covered
Why Data Engineering Tools Are Critical in 2025
- Explosion of AI/ML: Clean, structured data is the foundation for accurate ML models.
- Cloud Migration: Most enterprises are adopting multi-cloud strategies.
- Real-Time Demands: Businesses expect instant insights (fraud detection, personalization, IoT).
- Cost Optimization: Open-source vs SaaS trade-offs matter in budgeting.
Key Categories of Data Engineering Tools
1. ETL/ELT Platforms
ETL (Extract, Transform, Load) and ELT (Extract, Load, Transform) platforms automate the process of moving data from source systems into data warehouses. In ETL, data is transformed before loading, while in ELT, raw data is loaded into a warehouse first and transformed later.

Examples of Tools:
- dbt (Data Build Tool): SQL-based transformations inside warehouses.
- Fivetran: Automated ELT pipelines with hundreds of pre-built connectors.
- Talend: Enterprise-grade ETL and governance platform.
Key Features:
- Automates data extraction from APIs, SaaS tools, and databases.
- Supports schema mapping, data cleaning, and quality checks.
- Integrates with cloud warehouses like Snowflake, BigQuery, Redshift.
- Reduces manual scripting for data movement.
Use Cases:
- Consolidating marketing data from Google Ads, Facebook Ads, and LinkedIn.
- Integrating financial data from Stripe, QuickBooks, and PayPal.
- Preparing analytics-ready tables for dashboards in Looker or Power BI.
Related readings:- Introduction to Microsoft Power BI Platform
2. Data Warehousing
Data warehouses are central repositories where structured and semi-structured data is stored for analysis. They enable organizations to query massive datasets efficiently, run reports, and power BI dashboards.

Examples of Tools:
- Snowflake: Cloud-native warehouse with multi-cloud support.
- Amazon Redshift: AWS’s scalable warehouse for analytics.
- Google BigQuery: Serverless warehouse with built-in ML capabilities.
Key Features:
- Columnar storage for high-performance querying.
- Elastic scaling to handle terabytes or petabytes of data.
- Support for semi-structured data like JSON and Parquet.
- Integration with BI tools (Tableau, Looker, Power BI).
Use Cases:
- E-commerce companies analyzing clickstream data.
- Healthcare firms storing patient data securely for compliance.
- Financial institutions running fraud detection and risk analysis.
Related readings:- Snowflake vs Databricks vs AWS Redshift vs Azure Synapse
3. Workflow Orchestration
Workflow orchestration tools manage the order, dependencies, retries, and monitoring of data pipelines. Instead of manually scheduling scripts, orchestration platforms ensure pipelines run reliably and alert engineers when failures occur.

Examples of Tools:
- Apache Airflow: DAG-based orchestration with rich community support.
- Prefect: Lightweight, Python-native alternative to Airflow with better error handling.
Key Features:
- DAGs (Directed Acyclic Graphs) to visualize and manage workflows.
- Retry mechanisms for failed jobs.
- Monitoring dashboards for pipeline health.
- Integration with cloud services (AWS, GCP, Azure).
Use Cases:
- Running nightly ETL jobs that refresh dashboards.
- Scheduling ML model retraining workflows.
- Coordinating pipelines across multiple cloud services.
4. Real-Time Streaming
Real-time streaming tools handle continuous flows of data rather than static batches. These tools enable organizations to react instantly to events like user clicks, financial transactions, or IoT sensor data.

Examples of Tools:
- Apache Kafka: A distributed event streaming platform.
- Apache Flink: A low-latency stream processing engine.
Key Features:
- Millisecond-level latency.
- Fault-tolerant, distributed processing.
- Event-driven architecture for microservices.
- Scalable to millions of events per second.
Use Cases:
- Detecting fraudulent credit card transactions instantly.
- Powering real-time dashboards for stock trading platforms.
- Processing sensor data from smart homes, cars, and factories.
The 15 Best Data Engineering Tools for 2025
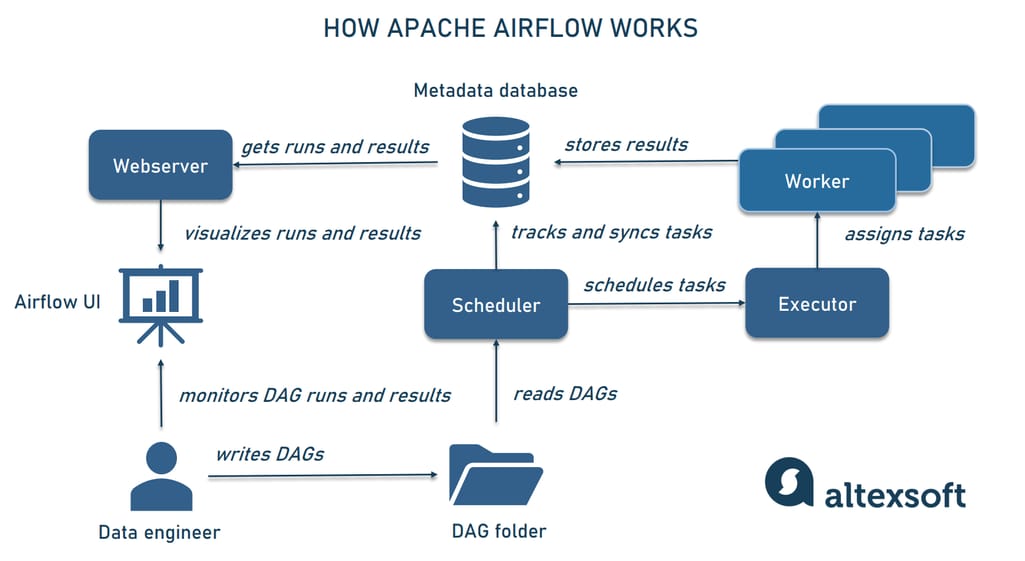
1. Apache Airflow – The Orchestration Standard
Apache Airflow, created at Airbnb, has grown into the industry standard for workflow orchestration. It allows data engineers to build pipelines as DAGs (Directed Acyclic Graphs), where each task represents a step in the data flow. Unlike cron jobs or manual scripts, Airflow offers monitoring, retry mechanisms, and detailed logging.
Source: Altexsoft
Key Features:
- Python-based configuration for flexibility.
- Seamless integrations with AWS (S3, Redshift), GCP (BigQuery, Dataflow), and Azure.
- Highly visual UI for pipeline monitoring.
- Strong community support with regular updates.
Use Cases:
- Automating daily ETL jobs.
- Scheduling ML training workflows
- Building end-to-end ETL pipelines.
- Automating reporting dashboards.
Why Popular in 2025:
Its adoption is so widespread that most job descriptions for data engineers list Airflow as a core requirement. With Kubernetes and cloud-native deployments, Airflow is now easier to scale than ever.
2. Apache Kafka – Real-Time Data Backbone
Apache Kafka is the most widely used streaming platform for handling high-throughput, real-time data. Originally developed at LinkedIn, it enables organizations to process millions of events per second with low latency. Kafka follows a publish-subscribe model, where producers publish events to topics, and consumers subscribe to those topics to process data.
Source: Google
Key Features:
- Distributed and fault-tolerant architecture.
- High scalability — easily supports thousands of producers and consumers.
- Integration with Spark, Flink, Hadoop, and machine learning workflows.
- Enterprise support available via Confluent Kafka.
Use Cases:
- Fraud detection in banking through real-time event monitoring.
- Order tracking in e-commerce platforms like Amazon.
- Streaming data from IoT sensors in smart devices.
- Log aggregation for DevOps and monitoring systems.
Why It Matters in 2025:
The world is becoming increasingly real-time. From financial markets to social media, decisions need to be instant. Kafka has become the backbone of event-driven architectures and is expected to remain critical for AI-powered systems that rely on live data streams.
3. Snowflake – The Cloud Data Warehousing Leader
Snowflake has disrupted the traditional data warehousing market with its cloud-native architecture. Unlike legacy systems, Snowflake separates compute and storage, allowing businesses to scale resources independently. It runs seamlessly on AWS, Azure, and GCP, giving enterprises flexibility in multi-cloud environments.

Key Features:
- Elastic scaling — handle petabytes of data without performance loss.
- Pay-as-you-go pricing model (great for cost optimization).
- Native support for structured and semi-structured data like JSON, Parquet, and Avro.
- Strong data governance, encryption, and role-based access.
- Secure data sharing between organizations.
Use Cases:
- Building enterprise data warehouses for large corporations.
- Running advanced analytics and business intelligence queries.
- Centralized storage for cross-departmental data sharing.
- Feeding clean data into ML/AI pipelines.
Why It Matters in 2025:
Snowflake continues to dominate as the fastest-growing warehouse solution. With organizations increasingly adopting multi-cloud strategies, its cross-cloud compatibility and serverless scaling make it one of the most future-proof choices.
Related readings:- Databricks vs Snowflake
4. Databricks – Unified Data + AI Lakehouse
Databricks, founded by the original creators of Apache Spark, is now one of the most important platforms for big data and AI workloads. It introduces the Lakehouse architecture, combining the flexibility of data lakes with the structured performance of warehouses.
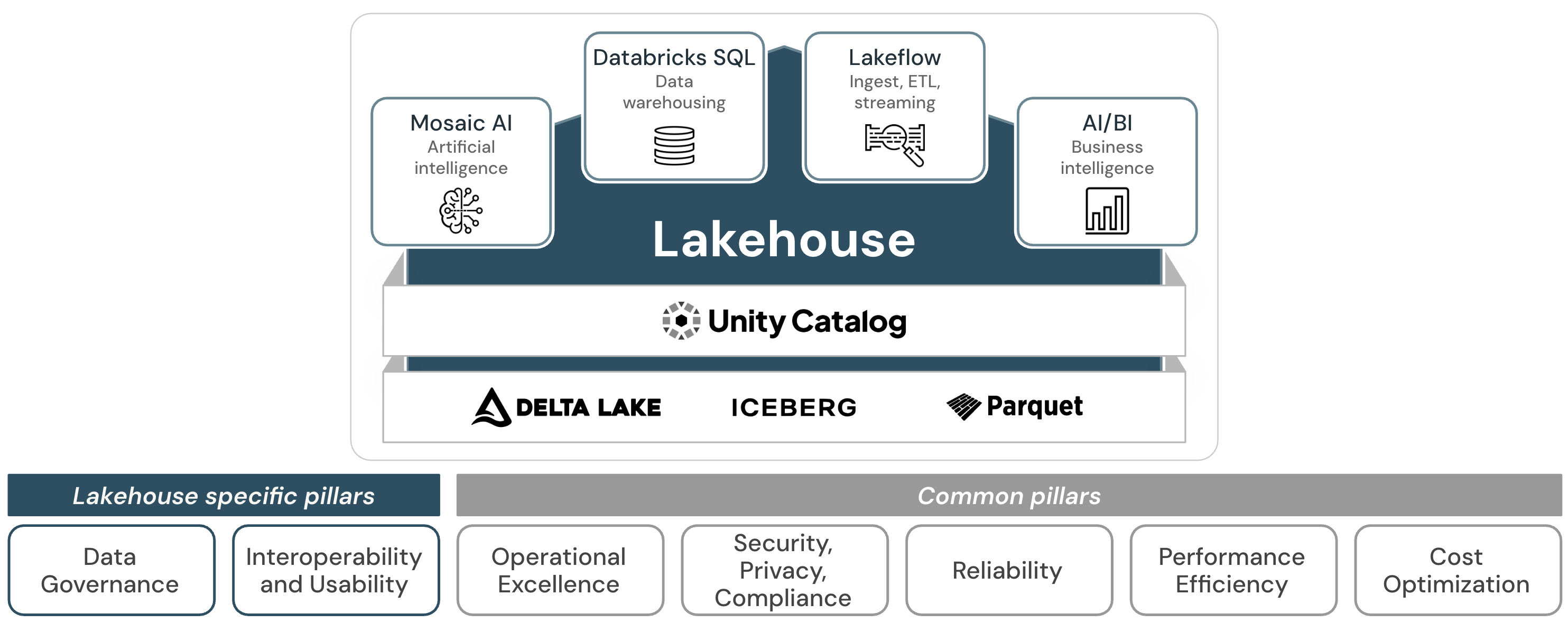
Key Features:
- Delta Lake for ACID transactions on big data.
- Built-in machine learning libraries (MLflow).
- Interactive workspace for engineers, analysts, and data scientists.
- Multi-cloud support across AWS, Azure, and GCP.
- Collaboration features like notebooks for shared workflows.
Use Cases:
- Training large-scale ML models with clean, versioned data.
- Real-time recommendation systems (e.g., for Netflix).
- Unified platform for data science and data engineering teams.
- Data governance and quality control at scale.
Why It Matters in 2025:
With AI becoming mainstream in business operations, Databricks enables teams to move from raw data to ML models seamlessly. It reduces silos between teams and has become a default choice for enterprises building AI-first products.
Related readings:- Mastering Databricks: A Comprehensive Guide to Learning and Interview Preparation
5. Apache Spark – Big Data Processing Powerhouse
Apache Spark remains the cornerstone of big data processing. It provides a fast, in-memory engine for both batch and streaming workloads. Spark supports multiple programming languages (Python, Scala, Java, R) and integrates with MLlib, GraphX, and structured streaming for diverse use cases.

Key Features:
- 100x faster than Hadoop MapReduce for in-memory computations.
- Supports distributed machine learning via MLlib.
- Stream processing for near real-time insights.
- APIs across multiple languages, lowering adoption barriers.
- Can run on-premises, on the cloud, or in hybrid setups.
Use Cases:
- Processing terabytes of data logs for analytics.
- Running ML pipelines for recommendation engines.
- Fraud detection in banking transactions.
- Predictive analytics in healthcare and retail.
Why It Matters in 2025:
Even with new platforms, Spark continues to be the backbone of enterprise big data ecosystems. Its open-source nature and adaptability mean Spark skills remain highly in demand for data engineers.
6. dbt (Data Build Tool) – SQL-Powered Transformations
dbt has transformed how data teams handle the “T” in ELT (Extract, Load, Transform). Unlike traditional ETL platforms, dbt lets engineers and analysts write transformations directly in SQL while version-controlling everything with Git. This makes transformations transparent, testable, and reproducible.

Key Features:
- SQL-first approach with Jinja templating for advanced logic.
- Built-in testing for data validation and quality checks.
- Auto-generated documentation for better collaboration.
- Seamless integration with warehouses like Snowflake, BigQuery, Redshift.
- Strong community support (dbt Slack, dbt Hub).
Use Cases:
- Defining company-wide metrics in a consistent, reusable way.
- Building analytics-ready datasets from raw warehouse tables.
- Enforcing data governance with tests and documentation.
Why It Matters in 2025:
dbt has become the bridge between analysts and engineers. Its ability to empower SQL users to manage production-ready transformations reduces reliance on heavy engineering, making it essential for agile data teams.
7. Fivetran – Fully Managed Data Pipelines
Fivetran simplifies ETL/ELT with its plug-and-play connectors. Instead of engineers writing custom scripts for every data source, Fivetran offers hundreds of pre-built integrations that automatically sync and update schemas.

Key Features:
- 400+ connectors for SaaS apps, databases, and APIs.
- Incremental updates instead of full refreshes (saves compute).
- Schema drift handling — automatic updates when source systems change.
- Strong security and compliance (SOC 2, GDPR).
Use Cases:
- Marketing teams syncing Google Ads, Facebook Ads, and HubSpot data.
- Finance teams consolidating Stripe, QuickBooks, and Salesforce.
- Enterprises automating ingestion into Snowflake or BigQuery.
Why It Matters in 2025:
As businesses adopt dozens of SaaS tools, manual ETL is no longer sustainable. Fivetran’s zero-maintenance pipelines let engineers focus on higher-value tasks.
8. Talend – Enterprise Data Integration & Governance
Talend is a veteran in the ETL space, offering data integration, governance, and quality solutions. Its cloud-native platform ensures enterprises can work across on-premise and cloud seamlessly.
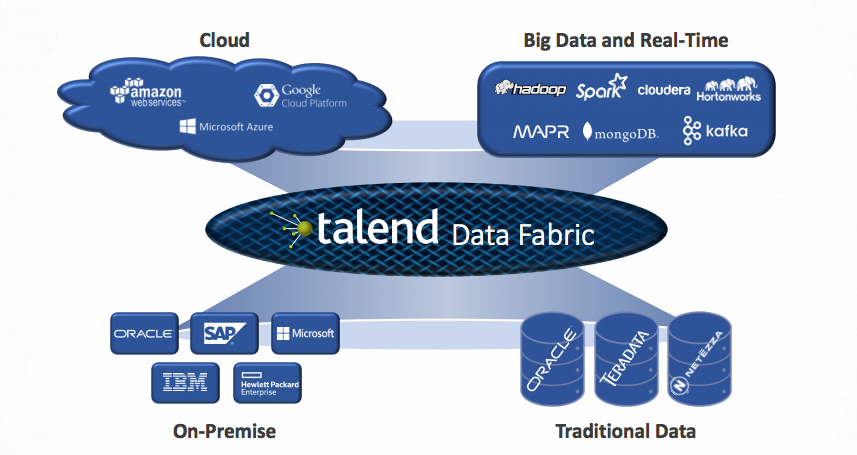
Key Features:
- Drag-and-drop ETL interface with advanced coding support.
- Data quality monitoring (detects duplicates, anomalies).
- APIs for third-party integration.
- Built-in data governance tools for compliance.
- Hybrid support (on-prem + multi-cloud).
Use Cases:
- Building enterprise-wide data integration pipelines.
- Enforcing compliance with GDPR, HIPAA, and financial regulations.
- Cleaning and preparing massive datasets for analytics.
Why It Matters in 2025:
In industries like healthcare, banking, and government, data quality and governance are as important as data itself. Talend remains a strong enterprise solution.
Related readings:- ETL Explained: Simplifying Data Transformation
9. Google BigQuery – Serverless Analytics at Scale
BigQuery is Google’s serverless, highly scalable data warehouse that allows users to run SQL queries on petabytes of data without managing infrastructure.

Key Features:
- Pay-per-query model — great for cost control.
- Integration with Looker Studio, Google Sheets, and AI tools.
- BigQuery ML for training ML models using SQL.
- Real-time streaming ingestion with Pub/Sub.
- Serverless architecture → zero infrastructure headaches.
Use Cases:
- Marketing attribution models using massive ad datasets.
- Predictive analytics directly in SQL (without external ML platforms).
- Enterprise dashboards using Looker Studio.
Why It Matters in 2025:
With AI natively integrated into Google Cloud, BigQuery is now more than a warehouse — it’s a prediction and analytics engine.
10. Amazon Redshift – AWS’s Analytics Workhorse
Amazon Redshift is a cloud-based data warehouse designed for large-scale analytics. It integrates seamlessly into the AWS ecosystem, making it a natural choice for AWS-heavy organizations.

Key Features:
- Columnar storage for fast query performance.
- Concurrency scaling for high query volumes.
- Redshift Spectrum to query data directly from Amazon S3.
- Deep integration with AWS services like SageMaker, Glue, and Lambda.
Use Cases:
- BI and reporting dashboards for retail and e-commerce.
- Processing clickstream data for personalization.
- Combining structured and semi-structured data (JSON, Parquet).
Why It Matters in 2025:
Redshift continues to evolve with serverless and ML integrations. For businesses already in AWS, Redshift is the most natural choice.
Related readings:- Snowflake vs Redshift : Modern-Day Data Warehouse Solutions
11. Microsoft Azure Data Factory – Hybrid ETL
Azure Data Factory (ADF) is a cloud-based ETL/ELT service by Microsoft. It provides a no-code UI for quick pipeline creation while still supporting complex transformations with custom scripts.

Key Features:
- 90+ pre-built connectors.
- Data Flow feature for visual ETL design.
- Orchestration across hybrid (on-prem + cloud) environments.
- Integration with Synapse Analytics and Power BI.
Use Cases:
- Migrating legacy data warehouses to the cloud.
- Building hybrid data pipelines.
- Feeding data into Azure ML and Power BI dashboards.
Why It Matters in 2025:
Enterprises using Microsoft products naturally choose ADF since it integrates with the entire Azure ecosystem.
12. Apache Flink – Next-Gen Stream Processor
Apache Flink is a stream processing framework that goes beyond Kafka by allowing stateful, event-time processing. It powers some of the lowest-latency systems in the world.

Key Features:
- Sub-second latency for processing streams.
- Stateful computations with exactly-once guarantees.
- Batch + stream unification in one engine.
- Integrates with Kafka, Hadoop, and cloud services.
Use Cases:
- Fraud detection in online banking transactions.
- Real-time personalization in e-commerce.
- IoT analytics for smart cities.
Why It Matters in 2025:
With the rise of real-time AI systems, Flink is gaining adoption in industries that demand ultra-low latency.
13. Prefect – Orchestration for the Modern Stack
Prefect positions itself as a “dataflow automation” tool, a modern alternative to Airflow. It provides a lightweight, Pythonic experience while offering cloud-based observability.

Key Features:
- Python-native API for defining workflows.
- Error handling and retries built-in.
- Prefect Cloud for monitoring and logs.
- Hybrid execution (local + cloud).
Use Cases:
- Data science workflows.
- ML model retraining pipelines.
- Cloud-native ETL orchestration.
Why It Matters in 2025:
As teams seek alternatives to Airflow’s complexity, Prefect has emerged as the developer-friendly orchestration tool.
14. Informatica – The Enterprise Data Integration Giant
Informatica has been a leader in data integration and governance for decades. While newer tools dominate startups, Informatica continues to be critical in large enterprises with strict compliance needs.

Key Features:
- Enterprise-grade Master Data Management (MDM).
- Metadata and lineage tracking.
- Cloud + on-prem hybrid support.
- AI-powered automation for ETL.
Use Cases:
- Regulatory compliance (GDPR, HIPAA).
- Data governance in banks and healthcare.
- Managing multi-department data warehouses.
Why It Matters in 2025:
Despite competition, Informatica remains the go-to tool for Fortune 500 companies with complex governance requirement.
15. Meltano – The Open Source Challenger
Meltano is an open-source ELT tool originally built at GitLab. It offers developers flexibility, transparency, and control that proprietary SaaS ETL tools often lack.

Key Features:
- Singer taps for extracting data from APIs.
- Git-based workflows for CI/CD pipelines.
- Plugin system for extensibility.
- Self-hosted or cloud-based deployment.
Use Cases:
- Startups building DIY data pipelines.
- Developers avoiding vendor lock-in.
- Custom data integrations for niche APIs.
Why It Matters in 2025:
In a world dominated by SaaS, Meltano provides an open-source alternative that appeals to engineering-driven organizations
Comparison Table
How to Choose the Right Tool
- For startups: dbt + Fivetran + BigQuery → quick setup.
- For enterprises: Airflow + Kafka + Snowflake + Informatica.
- For AI-focused teams: Databricks + Flink + Spark.
Conclusion
In 2025, data engineering tools are more powerful, automated, and cloud-native than ever. By mastering tools like Airflow, dbt, Snowflake, and Kafka, engineers can build scalable, real-time, and cost-efficient pipelines.
FAQ:
Next Task For You
join our Azure Data on Cloud Job-Oriented training program, we will cover 50+ Hands-On Labs. If you want to begin your journey towards becoming a Microsoft Certified and Get High-Paying Jobs check out our FREE CLASS.









![Microsoft Agentic AI Business Solutions Architect [AB-100] | K21 Academy](https://test.k21academy.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/11/Microsoft-Agentic-AI-Business-Solutions-Architect-AB-100-Exam-Overview1.png)



