![]()
AWS Lake Formation is a fully managed service that simplifies the creation, security, and management of data lakes. Many of the complex manual tasks necessary to construct data lakes are simplified and automated by Lake Formation. These processes include gathering, cleansing, transferring, and cataloguing data, as well as securely delivering that data for analytics and machine learning.
Lake Formation has its own permissions model that works in tandem with the IAM permissions model. This centrally established permissions architecture, similar to a relational database management system (RDMS), offers fine-grained access to data stored in data lakes via a simple grant or revoke method. Permissions for Lake Formation are enforced utilizing granular controls at the column, row, and cell levels across AWS analytics and machine learning services such as Amazon Athena.
In this blog, we will discuss AWS Lake Formation:
- Data Lakes: What They Are and Why We Need Them
- How does it work?
- What does the AWS Lake Formation include?
- AWS Data Lake Architecture
- Functionality
- Pricing
- FAQ’S
Data Lakes: What They Are and Why We Need Them
Many of you are unlikely to have heard of the term “data lake,” so let’s start there. A data lake is a centralised data repository that can hold all of your data (structured or unstructured) at any scale. A data lake may appear to be a chaotic environment, but it is not. A data lake comprises useful (or potentially valuable) information, as well as a screening procedure to ensure that no garbage is preserved.
Data lakes can be incredibly beneficial in discovering opportunities for corporate growth and enhancing productivity. It can help you better your Research and development decisions by allowing your teams to test and analyze their concepts. You may also raise customer happiness by merging a variety of client data, such as buying history and social media inputs.
 How does Lake Formation work?
How does Lake Formation work?
The Amazon Web Services (AWS) Lake Formation function allows you to create a secure data lake in a matter of days with minimal effort and time. Both of these versions of your data are available at all times. It is password-protected, centralized, and curated. You can potentially gain insights and make better business decisions by breaking down data silos and combining different types of analytics in a data lake.
Lake Formation makes it simple to create data lakes by simply specifying the data sources to be used as well as the access and security policies that will be applied to the lake. Lake Formation will assist you in moving the data into your new Amazon Simple Storage Service (S3) data lake, cleaning and classifying your data using machine learning algorithms, and securing access to your sensitive data with granular controls at the column, row, and cell levels once you have collected and catalogued data from databases and object storage.

What does the AWS Lake Formation include-
- Import data from existing databases: The data is scanned when you give AWS Lake Formation the location of your present databases and your login information.
- Organize and label your data: Lake Formation offers a collection of technical metadata that has been extracted from your data sources to consumers looking for datasets.
- Data transformation: Transformations like rewriting date formats to guarantee uniformity are possible with the help of Lake Formation. Amazon data lake Formation creates transformation templates and arranges the processes that will do so.
- Enforce encryption: Your data lake is encrypted with Amazon S3’s encryption via Lake Formation. To prevent malicious data removals in transit, you can use separate accounts for the source and destination regions when using S3.
- Manage access controls: Lake Formation allows you to manage access permissions for data in your data lake from a single location. Access to data can be restricted at the database, table, column, row, and cell levels using security rules. These policies apply to IAM users and roles, as well as users and groups federated via an external identity provider.
- Set up audit logging: Monitoring data access across analytics and machine learning platforms is possible using Lake Formation.
- Regulated tables: Accurately injecting ACID transactions into Amazon S3 tables is possible. Since Governed Table transactions instantly correct discrepancies and errors, all users see the same data.
- Data meta-tagging for business: In Data Lake on Amazon you can define appropriate use cases and data sensitivity levels using formation security and access restrictions.
- Allow self-service: Lake Formation offers self-service data lake access. Access rights can be granted or refused for tables established in the central data catalogue.
- Find data for analysis: Users of Lake Formation have access to text searches performed online for searching and filtering datasets stored in a common data library.
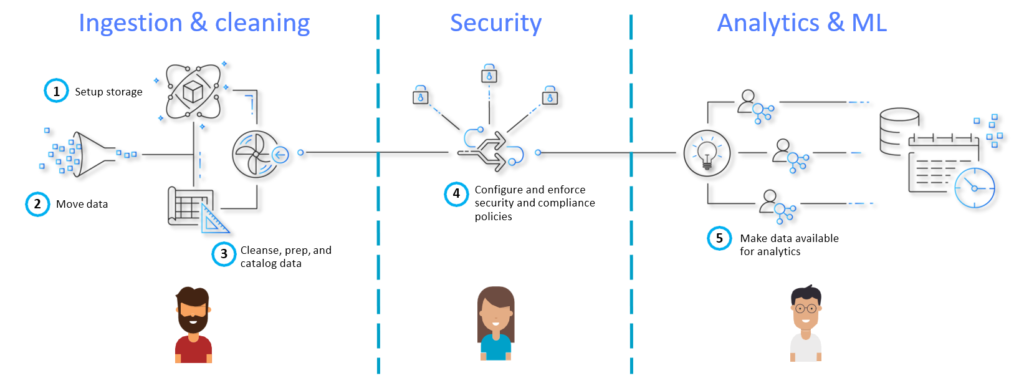
AWS Data Lake Architecture
Large amounts of unstructured data can be stored in object storage like Amazon S3 in Amazon Data Lake without being pre-structured, with the possibility to do future ETL and ELT on the data.
As a result, it is ideal for businesses that need to analyze highly large or frequently changing datasets.
Although there are various distinct data lake architectures, Amazon offers a standard architecture that has the following components:
- Irrespective of size, stores datasets on Amazon S3 in their original form.
- Utilizing AWS Glue and Amazon Athena, on-the-fly adjustments and analyses are carried out.
- Stores user-defined tags in Amazon Dynamo DB to contextualize datasets, enabling the application of governance policies and metadata-based dataset browsing.
- A pre-integrated data lake with SAML providers like Okta and Active Directory is created using federated templates.
The architecture is composed of 3 major components:
- Landing zone – Takes in raw data from numerous sources both inside and outside the company. No data transformation or modelling is done.
- Curation zone – You perform extract-transform-load (ETL) at this step, crawl data to identify its structure and value, add metadata, and use modelling techniques.
- Production zone – Consists of processed data that can be used directly by analysts or data scientists, or by business apps.

Functionality-
You can use Lake Formation as a tool to help you with the creation, security, and management of your data lake. Finding any existing data storage, whether it be in S3, a relational database, or a NoSQL database, should be your first step. Then, you should move the data into your data lake. Lake Formation is responsible for managing all of the tasks listed in the orange box, as well as for connecting those tasks with the data repositories and services listed in the blue box.
Create data lakes quickly: Using Data Lake Formation, you can now create data lakes in a lot less time than in the past and transport, store, categorize, and clean data much more easily. A new data lake hosted on Amazon S3 will be created by Lake Formation by automatically crawling all of your data sources.
Simplify the management of security: All users and services that access your data can have their access to tables, columns, rows, and cells defined and enforced by Lake Formation. All AWS services, including Redshift, Athena, AWS Glue, and EMR for Apache Spark, are implemented with uniform regulations.
Self-service data access: Using Data Lake Formation, you can create a data catalogue that includes all datasets and the people who have access to them. Helping your users find the most relevant data for their analysis leads to increased productivity.
Pricing of Lake Formation
AWS Lake Formation includes access controls based on databases, tables, columns, and tags at no extra cost. Governed Tables make it simple to make accurate changes to a large number of tables while maintaining a consistent view for all users.
Transaction metadata must be saved in order to manage concurrent transactions and roll back to an earlier table version. You must pay for transaction requests and metadata storage. The Lake Formation Storage API analyses the data stored in Amazon S3 and applies row and cell filters before delivering the results to apps. This screening is free of charge.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1. What challenges do organizations face when building and managing data lakes?
Organizations face challenges such as integrating diverse data sources, managing both structured and unstructured data, ensuring accurate data preparation, and maintaining security and governance to comply with regulations.
Q2. What best practices are recommended for building a data lake on AWS with Lake Formation?
Recommended practices include designing a scalable architecture, using Lake Formation blueprints for data ingestion, implementing fine-grained access controls and encryption, and leveraging AWS tools like S3, Glue, and Athena for efficient operations
Q3. What are the advantages of Amazon Athena for querying data lakes?
Amazon Athena offers serverless, cost-effective querying with high-speed performance, support for multiple data formats, built-in security, and seamless integration with other AWS tools.
Q4. What are the requirements for establishing a data lake with AWS Lake Formation?
To establish a data lake, you need an AWS account, an S3 bucket, IAM permissions, a Glue Data Catalog, encryption keys, and ETL tools for data integration and processing
Related Links/References
- AWS Free Tier: Create an Account
- AWS Free Tier Limits
- AWS Free Tier Account Details
- Amazon Athena
- AWS Glue
- What is AWS Kinesis (Amazon Kinesis Data Streams)?
Next Task For You
Begin your journey toward becoming an AWS Data Engineering Program Bootcamp by clicking on the below image and joining the waitlist.







![Microsoft Agentic AI Business Solutions Architect [AB-100] | K21 Academy](https://test.k21academy.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/11/Microsoft-Agentic-AI-Business-Solutions-Architect-AB-100-Exam-Overview1.png)



